Table of Contents
Are you happy with your Internet service?

About the author
James Murray
Watch our provider review videos
Video ReviewsWhich speed do I need?
Tell us what you use Internet for
How many users?
What Counts as High-Speed Internet?
This year, the median internet download speed in the USA is 242 Mbps. In general, an internet speed that surpasses 50 Mbps works fine for most online activities. But is it high-speed internet? It all depends on how you use your internet connection. Understanding what counts as high-speed internet will help you choose a good internet plan for you.
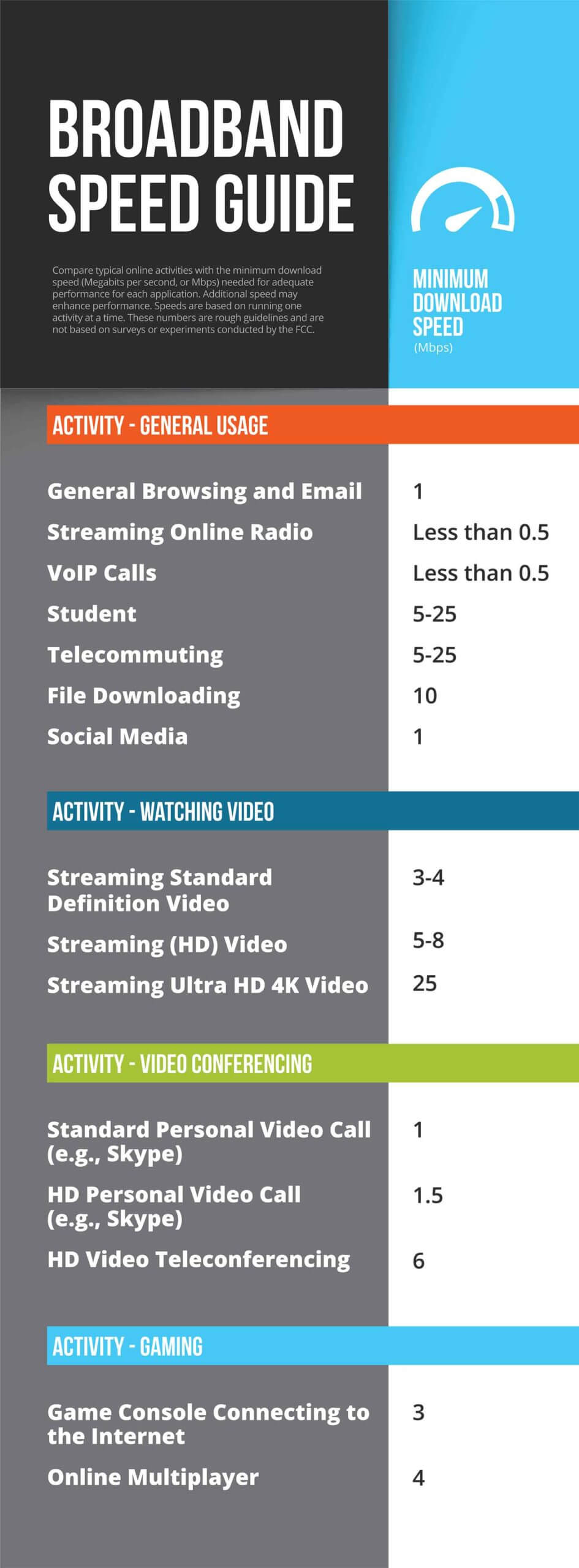
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) sets minimum standards as a guide for internet users to gauge their internet needs. The FCC recommends a minimum download speed of 4 Mbps for most online games with multiple players.
But people who actually play online games know that this 4 Mbps figure is unrealistically low. if your household has multiple devices and more than two users, a speed of 4 Mbps will not give you the bandwidth you need for smooth gaming. Download speed of 4 Mbps also won’t allow multiple users to stream in HD.
From 2015 to early 2024, the FCC had defined “high-speed internet" or broadband speed as 25 Mbps download/3 Mbps upload. It’s something of a mystery why the FCC set its recommended speeds so low for so many years.
But that has just changed. As of 2024, the FCC has revised the definition of high-speed internet up to 100 Mbps download/10 Mbps upload.
Basics of Internet Speeds
Experts measure internet speed with two terms: Mbps and Gpbs. The term “megabits per second" (Mbps) is the unit that measures the number of data packets that move in a second. The more Mbps an internet service provider can offer, the faster your internet speed will be. If the internet speed is very fast, it will go up to 1000 Mbps, also known as 1 Gigabit-per-second (Gbps)or 1 Gig.
Much of the time, ISPs will only mention one speed number, usually the download speed. But when you’re looking at high-speed internet plans, you’ll need to know the difference between download and upload speeds.
What is Download Speed?
A typical internet provider will only disclose the maximum download speeds in its internet plans. Download speeds determine how quickly your broadband internet connection can receive data from the web.
For example, when you’re web browsing, the download speed is how fast your computer loads the site so that you can view it. If you are streaming videos, fast download speeds will load the video within seconds without delays or lagging issues.
What is Upload Speed?
Upload speeds measure how quickly your broadband connection can send data from your connected devices to the internet. For example, if you want to upload a video to YouTube, your upload speed will determine how long it will take your internet connection to post the finished product.
According to the FCC, the minimum upload speed for broadband internet is 3 Mbps. But the minimum download speed that qualifies as high-speed internet is 25 Mbps. Clearly, even the FCC thinks download speeds need to be much faster than upload speeds.
Internet users usually demand more from a download speed than they do from an upload speed. A download speed is more important to the average user because most online activities depend on how quickly your connection can download data. Upload speeds often work fine at a lower rate for standard web browsing and email.
But lately, people have been paying more attention to upload speeds because of new technologies. Any activity that involves split-second interaction, such as videoconferencing or real-time gaming, needs faster upload speeds. Upload large files such as videos or graphics also needs more upload speed.

What Is Considered A Fast Internet Speed?
Now that you have a better understanding of how Internet speed varies with the type of Internet service, you will be able to get a better idea of what constitutes as “fast" Internet. A high-speed Internet connection depends on multiple factors.
- Type of Internet service
- Number of connected devices
- Number of users connected at one time
- Internet speed needs
Activities like online gaming and streaming HD videos will also make an impact on your Internet speeds, as they will require data to transfer at a quicker rate. As previously mentioned, the FCC benchmarked a speed of 25 Mbps as the minimum for downloads.
As you increase the number of devices connected and demand more speed out of your connection, a speed of 25 Mbps will not suffice. Here are some common speed tiers that are considered to provide fast Internet for multiple devices and users.
40 to 100 Mbps
This is a great middle-of-the-road fast Internet speed. If your Internet service provider can get you to a speed within this range, you’ll be able to:
- Engage in multiplayer online gaming
- Download large files
- Stream HD video on one or two devices
100 to 500 Mbps
Internet service providers that can guarantee Internet speeds within this range are great for households with multiple devices. This is especially true if you’re planning on performing real-time activities like online gaming. You can also:
- Stream UHD video on multiple screens
- Download large files within seconds
- Game online with multiple players
500 to 1,000 Mbps
This is the fastest Internet speed Internet providers can give you. Slow internet speeds are not an issue when your connection performs at 500 Mbps.
The one thing to keep in mind is that fast Internet speeds like these work better with fiber Internet. Not every high-speed Internet service can guarantee they’ll be able to deliver this type of high-speed Internet access.
If your Internet provider can, these are some of the tasks you’ll be able to perform without hiccups.
- Download high-resolution movies within minutes
- Video-conference in Ultra HD
- Complete smartphone’s operating system update in seconds.

What Is Normal High-Speed Internet?
A normal Internet speed is a speed that goes by the guidelines set up by the FCC. Although the FCC maintains that a minimum of 25 Mbps is a good Internet speed for most online activities, it’s not realistic to assume that most households will stick to such a low Mbps count.
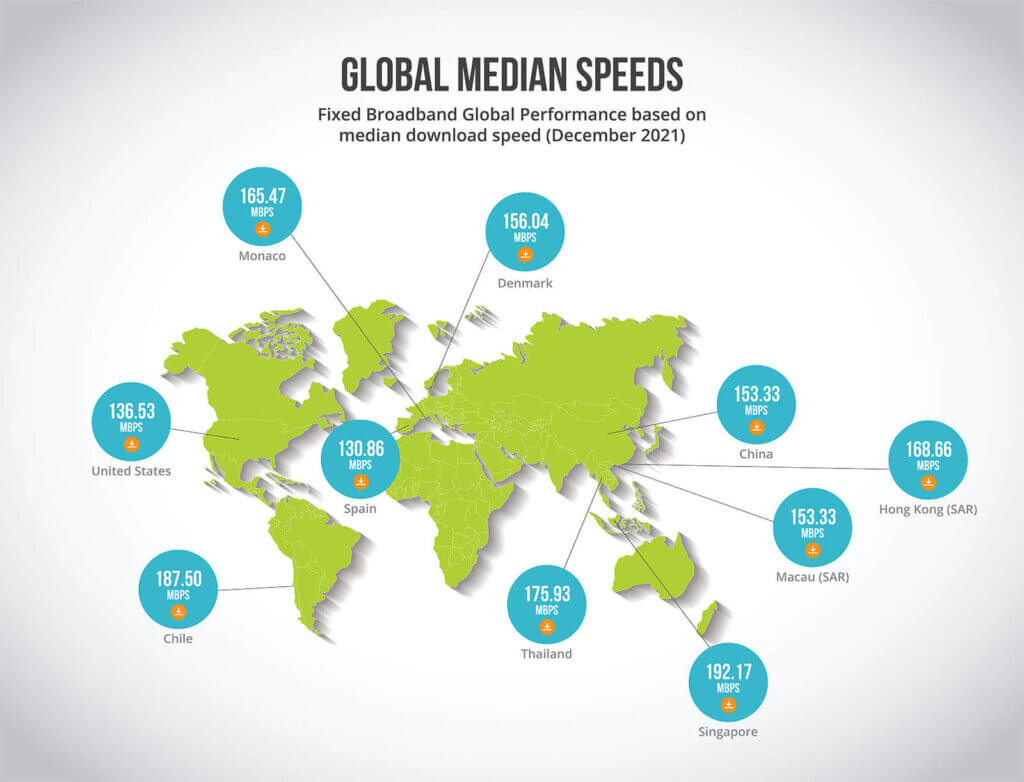
Based on a 2021 Internet speed test, the average broadband speed in the United States is 203 Mbps. Although the national speed average is not the fastest, it’s a speed that can support multiple connected devices without a problem.
Is 50 Mbps a Fast Internet Connection?
Internet providers that offer a speed of 50 Mbps offer a good Internet speed. But, it’s not necessarily considered a fast Internet connection. A speed of 50 Mbps, while still a good Internet speed, is on the lower tier of what comprises a fast Internet connection.
Is 100 Mbps Fast Internet Speed?
Yes, 100 Mbps is one of the best Internet speeds available. Anything that’s more than 100 Mbps is generally considered a high-speed Internet service.
Experts recommend higher speeds for users that have multiple devices and users that are constantly online. The best way to prevent slow speeds is to find an Internet plan that can accommodate the needs of everyone in the household.

How Do I Know if I Have High-Speed Internet?
The best way to figure out whether you have high-speed Internet or slow Internet is to run a speed test. Speed tests measure how quickly a device can upload and download information.
Fast Internet speeds will reflect speeds over 50 Mbps. Whereas slower download speeds will come up as anything that’s under 25 Mbps.
Different Internet providers offer a variety of plans that range in speed and data cap if any. Before conducting the speed test, make sure you take a look at the plan that you have in place with your provider to make sure that you know where your speed should be before running the test.
Tips to Get the Most Out of Your Speed Test Results
- Remember to restart your equipment. Most Internet providers advise their customers to restart their modem and router before they perform any other type of troubleshooting. This helps everything return to its full working status and gives you more accurate results.
- Don’t use your Internet for anything else during the test. Try to limit your Internet activities while you’re running the speed test so that the results don’t are less likely to show a slower speed. Examples of this are playing online games or connecting multiple devices.
- Clear your browser’s cache. Assuming you run the speed test multiple times in a row (and you should), clearing your browser’s cache can give you much more accurate results. Remember that a speed test works by downloading and uploading multiple files to test how fast your Internet is working. If you don’t clear your browser’s cache, there’s a chance you’ll get the same speed test results as before. This is because your computer might get confused and think that the files that the speed test is using already exist.
Recap
Remember that a fast Internet speed depends on multiple factors. Pay attention to your Internet plan and see if you have a data cap. If so, whenever you go over your monthly data limit, your provider might purposely slow down your Internet speed to keep you within set parameters.
Speeds over 50 Mbps are always good. But, the speeds that go beyond 500 Mbps are considered to be the absolute best and the fastest of all the Internet speeds available. And don’t forget to be patient when testing your speed. Take a deep breath and run the test multiple times for the best results.

About the author
